笔记
单击此处 下载完整的示例代码
transforms.offset_copy #
这说明了使用transforms.offset_copy进行转换,将绘图元素(例如文本字符串)定位在屏幕坐标(点或英寸)中相对于任何坐标中给定位置的指定偏移量处。
每个 Artist(Text、Line2D 等)都有一个可以在创建 Artist 时设置的变换,例如通过相应的 pyplot 函数。默认情况下,这通常是 Axes.transData 转换,从数据单元到屏幕像素。我们可以使用该offset_copy函数制作此转换的修改副本,其中修改包含偏移量。
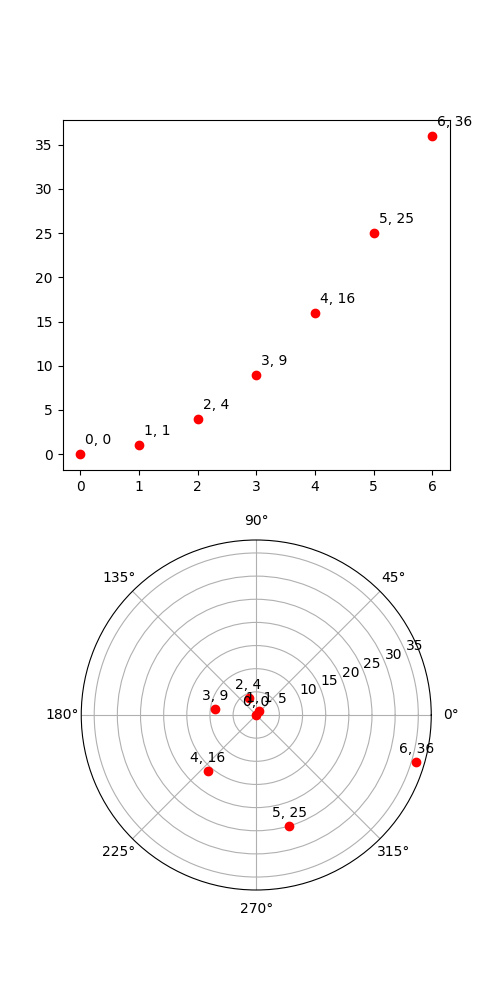
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.transforms as mtransforms
import numpy as np
xs = np.arange(7)
ys = xs**2
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(5, 10))
ax = plt.subplot(2, 1, 1)
# If we want the same offset for each text instance,
# we only need to make one transform. To get the
# transform argument to offset_copy, we need to make the axes
# first; the subplot function above is one way to do this.
trans_offset = mtransforms.offset_copy(ax.transData, fig=fig,
x=0.05, y=0.10, units='inches')
for x, y in zip(xs, ys):
plt.plot(x, y, 'ro')
plt.text(x, y, '%d, %d' % (int(x), int(y)), transform=trans_offset)
# offset_copy works for polar plots also.
ax = plt.subplot(2, 1, 2, projection='polar')
trans_offset = mtransforms.offset_copy(ax.transData, fig=fig,
y=6, units='dots')
for x, y in zip(xs, ys):
plt.polar(x, y, 'ro')
plt.text(x, y, '%d, %d' % (int(x), int(y)),
transform=trans_offset,
horizontalalignment='center',
verticalalignment='bottom')
plt.show()