笔记
单击此处 下载完整的示例代码
箱线图#
使用 matplotlib 可视化箱线图。
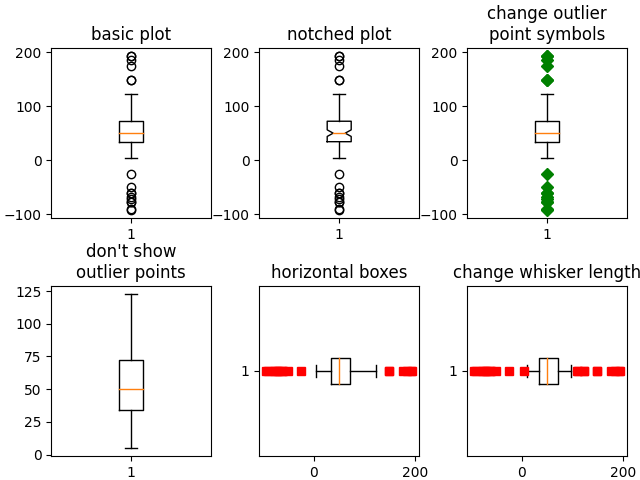
以下示例展示了如何使用 Matplotlib 可视化箱线图。有许多选项可以控制它们的外观以及它们用来汇总数据的统计信息。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from matplotlib.patches import Polygon
# Fixing random state for reproducibility
np.random.seed(19680801)
# fake up some data
spread = np.random.rand(50) * 100
center = np.ones(25) * 50
flier_high = np.random.rand(10) * 100 + 100
flier_low = np.random.rand(10) * -100
data = np.concatenate((spread, center, flier_high, flier_low))
fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 3)
# basic plot
axs[0, 0].boxplot(data)
axs[0, 0].set_title('basic plot')
# notched plot
axs[0, 1].boxplot(data, 1)
axs[0, 1].set_title('notched plot')
# change outlier point symbols
axs[0, 2].boxplot(data, 0, 'gD')
axs[0, 2].set_title('change outlier\npoint symbols')
# don't show outlier points
axs[1, 0].boxplot(data, 0, '')
axs[1, 0].set_title("don't show\noutlier points")
# horizontal boxes
axs[1, 1].boxplot(data, 0, 'rs', 0)
axs[1, 1].set_title('horizontal boxes')
# change whisker length
axs[1, 2].boxplot(data, 0, 'rs', 0, 0.75)
axs[1, 2].set_title('change whisker length')
fig.subplots_adjust(left=0.08, right=0.98, bottom=0.05, top=0.9,
hspace=0.4, wspace=0.3)
# fake up some more data
spread = np.random.rand(50) * 100
center = np.ones(25) * 40
flier_high = np.random.rand(10) * 100 + 100
flier_low = np.random.rand(10) * -100
d2 = np.concatenate((spread, center, flier_high, flier_low))
# Making a 2-D array only works if all the columns are the
# same length. If they are not, then use a list instead.
# This is actually more efficient because boxplot converts
# a 2-D array into a list of vectors internally anyway.
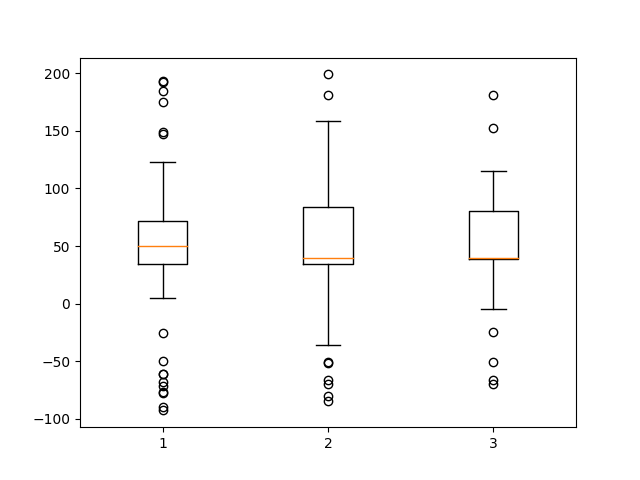
data = [data, d2, d2[::2]]
# Multiple box plots on one Axes
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.boxplot(data)
plt.show()
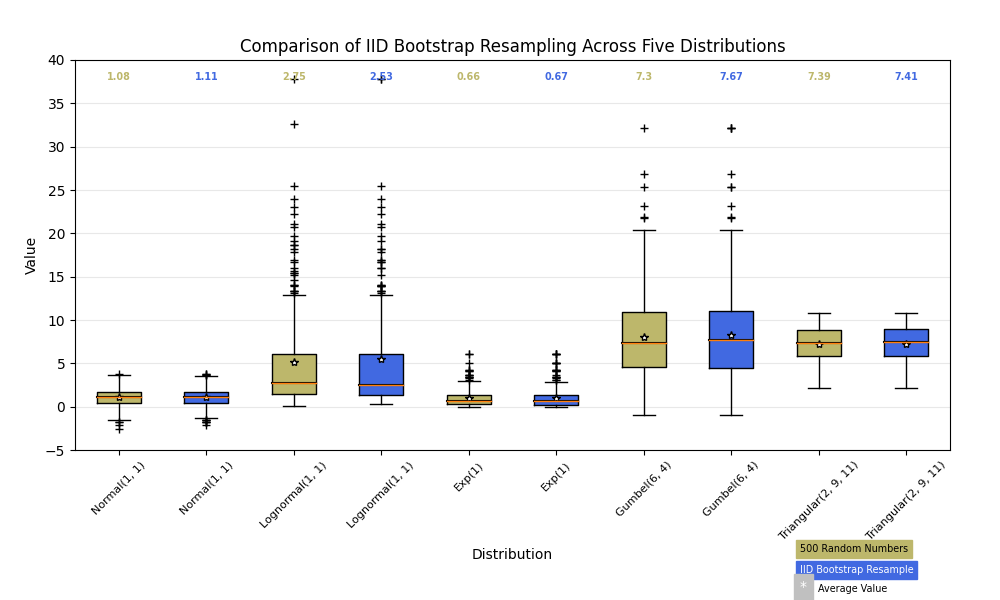
下面我们将从五个不同的概率分布中生成数据,每个概率分布都有不同的特征。我们想研究数据的 IID 引导重采样如何保留原始样本的分布属性,箱线图是进行此评估的一种可视化工具
random_dists = ['Normal(1, 1)', 'Lognormal(1, 1)', 'Exp(1)', 'Gumbel(6, 4)',
'Triangular(2, 9, 11)']
N = 500
norm = np.random.normal(1, 1, N)
logn = np.random.lognormal(1, 1, N)
expo = np.random.exponential(1, N)
gumb = np.random.gumbel(6, 4, N)
tria = np.random.triangular(2, 9, 11, N)
# Generate some random indices that we'll use to resample the original data
# arrays. For code brevity, just use the same random indices for each array
bootstrap_indices = np.random.randint(0, N, N)
data = [
norm, norm[bootstrap_indices],
logn, logn[bootstrap_indices],
expo, expo[bootstrap_indices],
gumb, gumb[bootstrap_indices],
tria, tria[bootstrap_indices],
]
fig, ax1 = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 6))
fig.canvas.manager.set_window_title('A Boxplot Example')
fig.subplots_adjust(left=0.075, right=0.95, top=0.9, bottom=0.25)
bp = ax1.boxplot(data, notch=False, sym='+', vert=True, whis=1.5)
plt.setp(bp['boxes'], color='black')
plt.setp(bp['whiskers'], color='black')
plt.setp(bp['fliers'], color='red', marker='+')
# Add a horizontal grid to the plot, but make it very light in color
# so we can use it for reading data values but not be distracting
ax1.yaxis.grid(True, linestyle='-', which='major', color='lightgrey',
alpha=0.5)
ax1.set(
axisbelow=True, # Hide the grid behind plot objects
title='Comparison of IID Bootstrap Resampling Across Five Distributions',
xlabel='Distribution',
ylabel='Value',
)
# Now fill the boxes with desired colors
box_colors = ['darkkhaki', 'royalblue']
num_boxes = len(data)
medians = np.empty(num_boxes)
for i in range(num_boxes):
box = bp['boxes'][i]
box_x = []
box_y = []
for j in range(5):
box_x.append(box.get_xdata()[j])
box_y.append(box.get_ydata()[j])
box_coords = np.column_stack([box_x, box_y])
# Alternate between Dark Khaki and Royal Blue
ax1.add_patch(Polygon(box_coords, facecolor=box_colors[i % 2]))
# Now draw the median lines back over what we just filled in
med = bp['medians'][i]
median_x = []
median_y = []
for j in range(2):
median_x.append(med.get_xdata()[j])
median_y.append(med.get_ydata()[j])
ax1.plot(median_x, median_y, 'k')
medians[i] = median_y[0]
# Finally, overplot the sample averages, with horizontal alignment
# in the center of each box
ax1.plot(np.average(med.get_xdata()), np.average(data[i]),
color='w', marker='*', markeredgecolor='k')
# Set the axes ranges and axes labels
ax1.set_xlim(0.5, num_boxes + 0.5)
top = 40
bottom = -5
ax1.set_ylim(bottom, top)
ax1.set_xticklabels(np.repeat(random_dists, 2),
rotation=45, fontsize=8)
# Due to the Y-axis scale being different across samples, it can be
# hard to compare differences in medians across the samples. Add upper
# X-axis tick labels with the sample medians to aid in comparison
# (just use two decimal places of precision)
pos = np.arange(num_boxes) + 1
upper_labels = [str(round(s, 2)) for s in medians]
weights = ['bold', 'semibold']
for tick, label in zip(range(num_boxes), ax1.get_xticklabels()):
k = tick % 2
ax1.text(pos[tick], .95, upper_labels[tick],
transform=ax1.get_xaxis_transform(),
horizontalalignment='center', size='x-small',
weight=weights[k], color=box_colors[k])
# Finally, add a basic legend
fig.text(0.80, 0.08, f'{N} Random Numbers',
backgroundcolor=box_colors[0], color='black', weight='roman',
size='x-small')
fig.text(0.80, 0.045, 'IID Bootstrap Resample',
backgroundcolor=box_colors[1],
color='white', weight='roman', size='x-small')
fig.text(0.80, 0.015, '*', color='white', backgroundcolor='silver',
weight='roman', size='medium')
fig.text(0.815, 0.013, ' Average Value', color='black', weight='roman',
size='x-small')
plt.show()
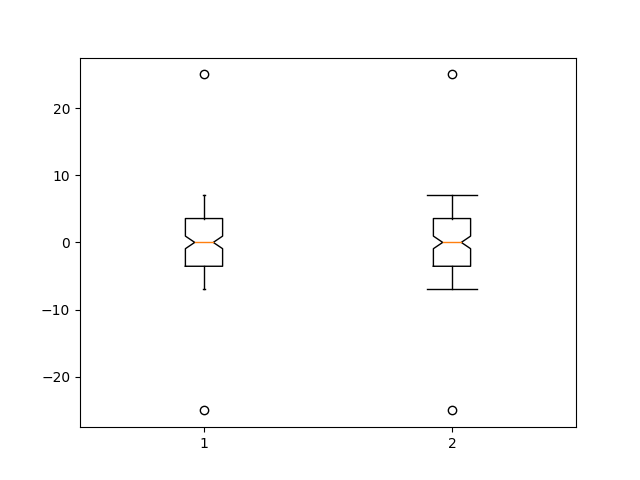
在这里,我们编写了一个自定义函数来引导置信区间。然后我们可以使用箱线图和这个函数来显示这些间隔。
def fake_bootstrapper(n):
"""
This is just a placeholder for the user's method of
bootstrapping the median and its confidence intervals.
Returns an arbitrary median and confidence interval packed into a tuple.
"""
if n == 1:
med = 0.1
ci = (-0.25, 0.25)
else:
med = 0.2
ci = (-0.35, 0.50)
return med, ci
inc = 0.1
e1 = np.random.normal(0, 1, size=500)
e2 = np.random.normal(0, 1, size=500)
e3 = np.random.normal(0, 1 + inc, size=500)
e4 = np.random.normal(0, 1 + 2*inc, size=500)
treatments = [e1, e2, e3, e4]
med1, ci1 = fake_bootstrapper(1)
med2, ci2 = fake_bootstrapper(2)
medians = [None, None, med1, med2]
conf_intervals = [None, None, ci1, ci2]
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
pos = np.arange(len(treatments)) + 1
bp = ax.boxplot(treatments, sym='k+', positions=pos,
notch=True, bootstrap=5000,
usermedians=medians,
conf_intervals=conf_intervals)
ax.set_xlabel('treatment')
ax.set_ylabel('response')
plt.setp(bp['whiskers'], color='k', linestyle='-')
plt.setp(bp['fliers'], markersize=3.0)
plt.show()

在这里,我们自定义 caps 的宽度。
x = np.linspace(-7, 7, 140)
x = np.hstack([-25, x, 25])
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.boxplot([x, x], notch=True, capwidths=[0.01, 0.2])
plt.show()
参考
此示例中显示了以下函数、方法、类和模块的使用:
脚本总运行时间:(0分3.038秒)